Solar water heaters have become increasingly popular as a sustainable way to heat water for various uses. Among the most common types are Flat Plate Collectors (FPC) and Evacuated Tube Collectors (ETC). Both have their own unique features, advantages, and disadvantages, making them suitable for different situations. This comprehensive guide will explore the differences between ETC and FPC solar water heaters, helping you decide which type is best for your needs.
Types of Solar Water Heaters
Solar water heaters generally fall into two main categories: Flat Plate Collectors (FPC) and Evacuated Tube Collectors (ETC). Let’s delve into each type to understand their construction, working principles, advantages, and disadvantages.
Flat Plate Collectors (FPC)
Flat Plate Collectors are effective and reliable systems for harnessing solar energy to heat water. Users can appreciate how these systems contribute to energy efficiency and sustainability by understanding their construction and working principles.
Construction and Components
Flat Plate Collectors are effective and reliable systems for harnessing solar energy to heat water. Users can appreciate how these systems contribute to energy efficiency and sustainability by understanding their construction and working principles.
Metal Plates: Typically made of copper or aluminum, these plates are coated with a selective material to maximize solar radiation absorption.
Transparent Cover: Usually made of glass or plastic, this cover allows sunlight to enter while reducing heat loss.
Insulation: Surrounds the metal plates to minimize heat loss and improve efficiency.
Casing: A durable outer shell that protects the internal components from environmental damage, ensuring the longevity of the collector.
FPC Solar Water Heater Working Principle
The working principle of Flat Plate Collectors involves several steps:
Absorption of Solar Radiation: Sunlight passes through the transparent cover and strikes the metal plates.
Heat Transfer: The selective coating on the metal plates absorbs the solar radiation and converts it into heat.
Fluid Heating: The absorbed heat is transferred to the water or heat transfer fluid flowing through the tubes attached to the plates.
Heat Storage: The heated fluid is then stored in an insulated tank for later use, providing a continuous hot water supply.
Diagram of Flat Plate Collectors (FPC)
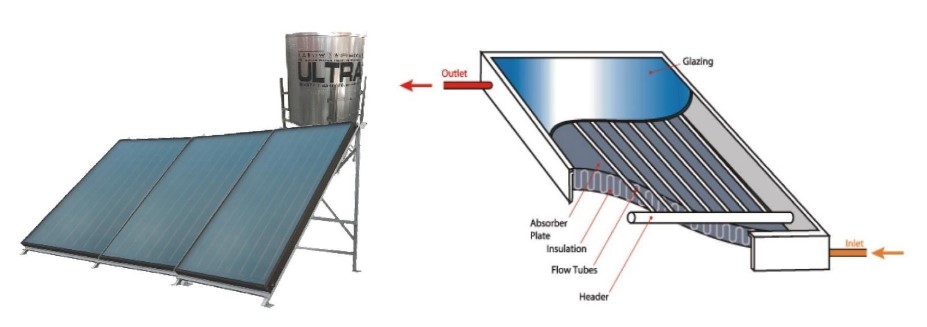
Detailed Explanation of The Working Principal of FPC Solar Water Heaters
Metal Plates: These plates act as the primary absorbers of solar energy. The selective coating ensures that a maximum amount of sunlight is absorbed and converted into heat while minimizing reflection losses.
Transparent Cover: This component is crucial for trapping heat within the collector. It allows sunlight to pass through but prevents the heat from escaping, thus increasing the overall efficiency of the system.
Insulation: The insulation material surrounds the metal plates and the entire collector. It plays a vital role in minimizing heat loss to the environment, ensuring that most of the captured heat is transferred to the fluid.
Casing: The casing not only provides structural support but also protects the internal components from weather-related damages such as rain, snow, and wind, thereby extending the lifespan of the collector.
Advantages of FPC Solar Water Heaters
Durable and Long-lasting: The robust construction ensures a long lifespan.
Performs Well in Direct Sunlight: High efficiency in sunny conditions.
Dis-advantages of FPC Solar Water Heaters
Less Efficient in Colder Climates: Performance drops significantly in colder or cloudy weather.
Heavier and Bulkier: Requires more space and stronger structural support.
Evacuated Tube Collectors (ETC)
Evacuated Tube Collectors are highly efficient solar water heating systems designed to operate effectively even in colder climates. By understanding their construction and working principles, users can appreciate how these systems maximize solar energy utilization while minimizing heat loss, making them an excellent choice for sustainable energy solutions.
Construction and Components
Evacuated Tube Collectors are designed to maximize the efficiency of solar energy collection by minimizing heat loss. They consist of several key components:
ETC Solar Water Heater Working Principle
The working principle of Evacuated Tube Collectors can be broken down into the following steps:
Solar Radiation Absorption: Sunlight passes through the transparent glass tubes and strikes the metal absorber tubes inside. The selective coating on the absorber tubes ensures that a high percentage of the solar radiation is absorbed and converted into heat.
Heat Retention: The vacuum between the glass tube and the absorber tube acts as an excellent insulator, reducing heat loss. This insulation ensures that most of the absorbed heat is retained within the system.
Heat Transfer: The heat absorbed by the metal tubes is transferred to the fluid (usually water or a heat transfer fluid) inside the tubes. The heated fluid rises due to the natural convection process.
Fluid Movement: The heated fluid moves to the top of the tube and into the manifold. The hot fluid is transferred from the manifold to the storage tank, where it is stored for later use.
Circulation: After losing its heat, the cooled fluid returns to the bottom of the tubes to be reheated, maintaining a continuous cycle of heating and circulation.
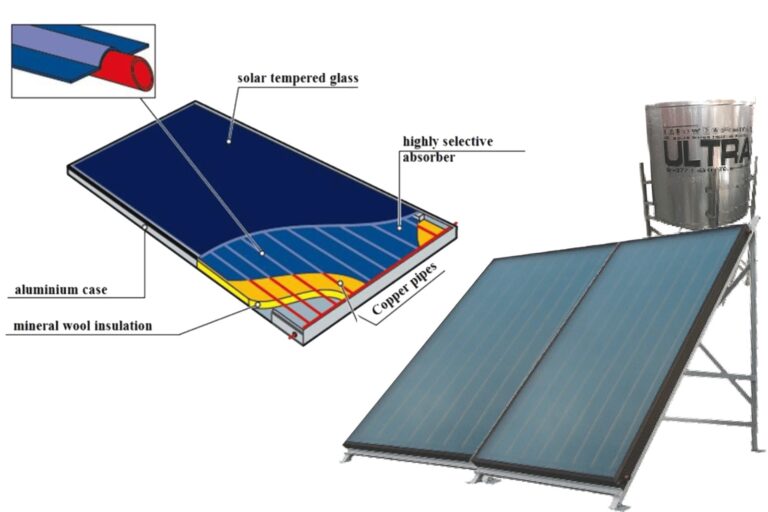
Detailed Explanation of The Working Principal of ETC Solar Water Heaters
Glass Tubes: The outer glass tubes are transparent to solar radiation but act as a barrier to heat loss. This transparency ensures maximum sunlight enters the tube.
Vacuum: By eliminating air between the glass and the absorber, the vacuum prevents heat loss through conduction and convection, keeping the absorbed heat within the system.
Absorber Coating: This special coating is designed to capture and convert as much solar energy as possible while reflecting very little.
Manifold: The manifold collects the heated fluid and transfers it efficiently to the storage tank, ensuring a constant hot water supply.
Advantages of ETC Solar Water Heaters
Highly Efficient: Works well even in cold and cloudy conditions.
Lighter and Easier to Install: Easier to handle and install than FPCs.
Dis-advantages of ETC Solar Water Heaters
More Fragile: The glass tubes are more prone to damage.
Can Be More Expensive: Initial costs can be higher compared to FPCs.
Comparison Between FPC and ETC Solar Water Heaters
| Criteria | FPC (Flat Plate Collector) | ETC (Evacuated Tube Collector) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally has a lower initial cost but may incur higher long-term maintenance costs. | Higher initial investment but lower maintenance costs over time. |
| Durability | More durable and long-lasting, with less susceptibility to damage. | While efficient, the glass tubes can be fragile and more susceptible to damage. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning and maintenance to ensure efficiency. | Lower maintenance needs but requires careful handling to avoid damaging the glass tubes. |
| Installation | Bulkier and heavier, requiring more structural support and space. | Lighter and easier to install, making it suitable for various types of roofs. |
| Applications and Suitability |
|
|
Final Say
Both Flat Plate Collectors (FPC) and Evacuated Tube Collectors (ETC) have strengths and weaknesses. The choice depends on specific needs, climate conditions, and budget to afford the price of the solar water heater.
FPCs are durable and perform well in sunny climates, while ETCs offer higher efficiency and better performance in colder and cloudy conditions. Consider these factors carefully to select the best solar water heating system for your requirements.